Mounting Datasets to a Compute Instance in Azure Machine Learning
Table of Contents
Introduction #
This post outlines how you can mount a Dataset to a Compute Instance in Azure Machine. This can help exploring file-based datasets in Jupyter, especially for large datasets where download to the disk of the Compute Instance is impractical. Furthermore, this method can also help during exploration phase, where you probably want to read only a subset of the data.
Prerequisites #
All we need to get started is a Workspace with a file-based Dataset, as well as a Compute Instance. Im testing this on a STANDARD_DS3_V2 instance in West Europe.
Mounting a Dataset to a Compute Instance #
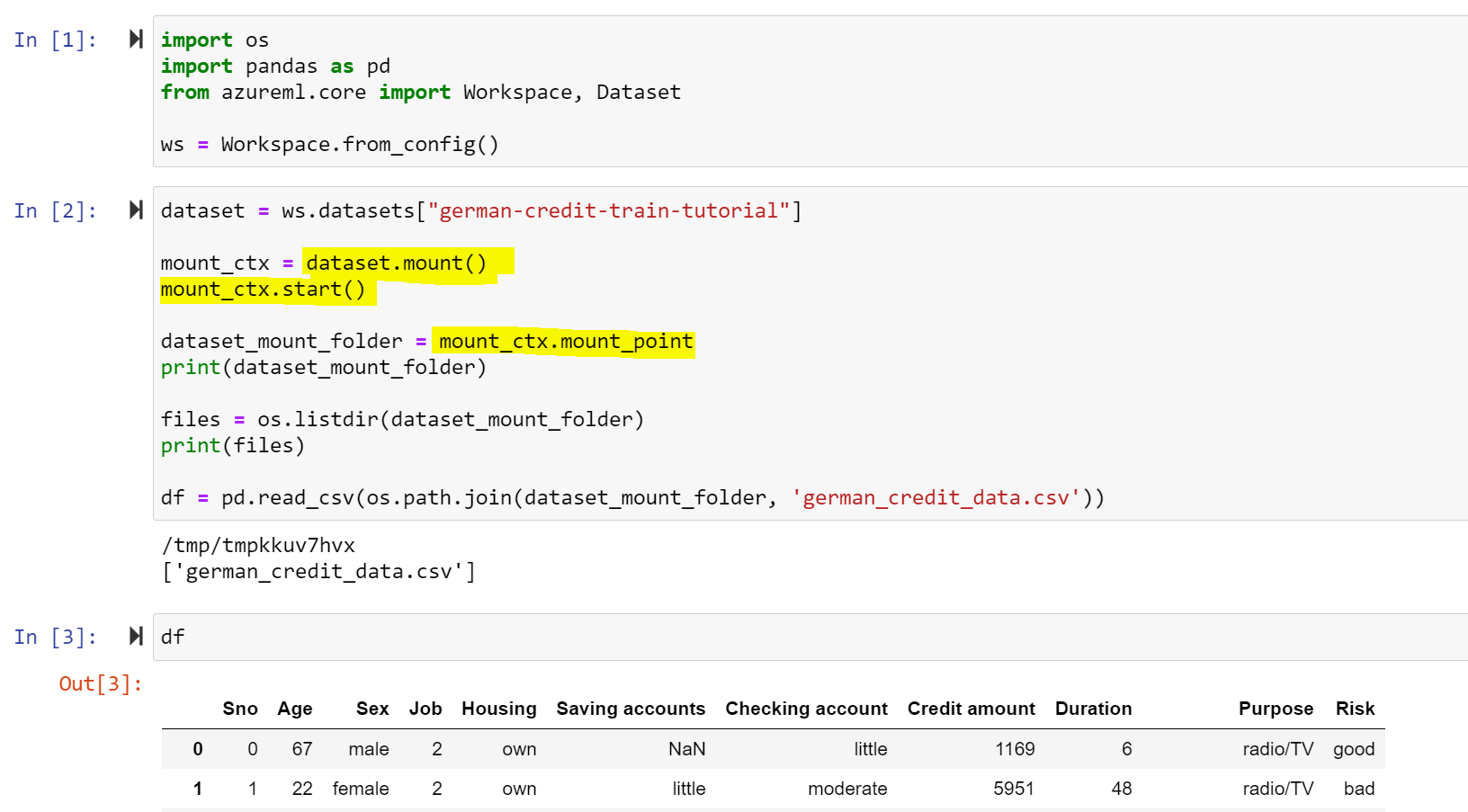
Lets start up Jupyter or JupyterLab on the Compute Instance. You can execute the following code to mount the dataset to the machine, access the data, and then later unmount it:
import os
import pandas as pd
from azureml.core import Workspace, Dataset
# Connect to Workspace and reference Dataset
ws = Workspace.from_config()
dataset = ws.datasets["german-credit-train-tutorial"]
# Create mountcontext and mount the dataset
mount_ctx = dataset.mount()
mount_ctx.start()
# Get the mount point
dataset_mount_folder = mount_ctx.mount_point
print(dataset_mount_folder)
# List the files in the mount point
files = os.listdir(dataset_mount_folder)
print(files)
# Read some data
df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(dataset_mount_folder, 'german_credit_data.csv'))
# Do some more stuff with the data....
# Unmount the dataset from the instance
mount_ctx.stop()
If you want to mount the dataset to a specific folder, you can also specify the mount path, e.g., mount(mount_point='/mnt/dataset1'). In this case, the path already needs to exist. See the API documentation for more details.
In case you forget to stop the mount context (i.e., unmounting it), no worries! You can also do it from the command line later:
azureuser@clemens-vm:/$ mount | grep /tmp
_DPrepFuse on /tmp/tmp89tgbd31 type fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1001,group_id=1002)
azureuser@clemens-vm:/$ sudo umount /tmp/tmp89tgbd31
azureuser@clemens-vm:/$ mount | grep /tmp
Restarting the Compute Instance will also remove the mount. Azure Machine Learning uses fuse to mount the Storage Account. Therefore, there is no drawback on the Storage Account in case you forget to unmount it. The dataset is mounted as read-only, there you cannot cause any inconsistencies anyway.
Performance #
In my quick test, I was using a 10 GB file in Blob Storage and just read it into the Compute Instance:
$ dd if=test_10gb.tmp of=/dev/null bs=64k
163840+0 records in
163840+0 records out
10737418240 bytes (11 GB, 10 GiB) copied, 89.567 s, 120 MB/s
The results are very much in line with the expected performance for reading a single file in Blob (Standard tier). Typically, we should see around ~80-120MB/s per file (sometimes even a bit more). Reading files in parallel, leveraging Premium Blob, ADLSg2, or using a larger Compute Instance size, etc. could obviously improve performance even more.
Summary #
Mounting a Dataset to a Compute Instance in Azure Machine Learning is easy and can dramatically help during data exploration and when dealing with large datasets.
Stay safe and let me know if you have any questions!